HISTORY OF SAS :
- SAS once stood for “Statistical Analysis System,” But now it is only SAS.
- SAS began at North Carolina State University as a project to analyze agricultural research. Founded in 1976 to help all sort of customers.
- SAS is both software and company.
- The World biggest private sector company.
SAS giving operations in various sectors like,
Automotive
Communications
Educations
Banking/Financial Services
Government
Health Insurance
Health Care Providers
Hospitality & Entertainment
Insurance
Life Sciences
Manufacturing
Media
Oil & Gas
Retail
Hostels
Utilities
And giving solution lines as
Analytics
Business Intelligence
Customer Intelligence
Data Integration & ETL
Financial Intelligence
Foundation Tools
Fraud Management
Governance, Risk & Compliance
High-Performance Computing
Human Capital Intelligence
IT Management
On Demand Solutions
Performance Management
Risk Management
Supply Chain Intelligence
Sustainability Management
In 1966, there was no SAS.
But there was a need for a computerized statistics program to analyze vast amounts of agricultural data collected through
United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) grants.
Then research started by University Statisticians Southern Experiment Stations, Eight land-grant universities that received the majority of their research funding from the USDA. And some schools came together under a grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to develop a general-purpose statistical software package to analyze all the agricultural data they were generating.
North Carolina State University, located in the capital city of Raleigh, North Carolina became the leader in the consortium.
North Carolina State University faculty members
Jim Goodnight and Jim Barr
Emerged as the project leaders –
Barr creating the architecture and
Goodnight implementing the features
In 1972 NIH stopped to give funds to this team, then the consortium agreed to chip in $5,000 apiece each year to allow NCSU to continue developing and maintaining the system and supporting their statistical analysis needs.
During the coming years, SAS software was licensed by pharmaceutical companies, insurance companies and banks, as well as by the academic community that had given birth to the project.
Jane Helwig, another Statistics Department employee at NCSU, Joined the project consortium as documentation writer
John Sall, a graduate student and programmer, rounded out the core team
Incorporation
In 1976 Goodnight, Barr, Helwig and Sall left NCSU and formed
SAS Institute Inc. – a private company “devoted to the maintenance and further development of SAS.” They opened offices in a building #2806 Hillsborough Street, across from the university.
By 1980, the growing company building capacity is not sufficient in Hillsborough Street building, and then it’s moved to the site of its present headquarters offices just outside Raleigh in Cary, North Carolina. In that time employs were 20.
In this time SAS was growing, the entire computer hardware and software industry was changing, with new operating systems and platforms placing new demands on software developers one of the first steps for SAS was to adapt the software to operate on IBM’s Disk Operating System (DOS).
Now it is working on different operating systems like windows, Dos, Z/OS, UNIX and various UNIX flavors.
In 1990 SAS Company grow with employ force of 7000.
SAS celebrated its 25th anniversary in 2001,
Its turn out from various difficulties along with the millennium and the Y2K frenzy. And they created new logo and tagline presently which we are seeing Tagline is –
THE POWER TO KNOW®
SAS has been named one of FORTUNE magazine’s “100 Best Companies to Work For” every year since 1998 and no1 in 2010
SAS named the best company to work for in 2010 by FORTUNE.
SAS IS MULTI VENDOR ARCHITECTURE
Multi Vendor Architecture is the foundation of the cross-platform portability and Interoperability of the SAS system means it allows programs to be written once and run anywhere, regardless of hardware or operating system. This architecture provides customers with hardware independence and a flexible implementation.
SAS IS MULTI DATABASE ARCHITECTURE
SAS can connect to any kind of data source to read the data, that’s why SAS is Multi Database Architecture.
Data sources are databases (like Oracle, SQL Server, DB2, Sybase, Teradata, Informix and MS-Access etc…)
Or Files (like Excel, CSV, and Notepads etc…)
THE PURPOSE OF SAS
SAS is Flexible and extensible fourth-generation programming language designed for data access, transformation and reporting
-> Data access and Data Management
-> User Interfaces
-> Application Development
-> Business Solutions
-> ETL
-> Analytics
-> Report & Graphics
SAS-FUNCTIONALITY
The functionality of the SAS System is built around the four data-driven tasks.
1. Data access
2. Data management
3. Data analysis
4. Data presentation.
Data access:
Addresses the data required by the application.
It means reads raw data from source to SAS application.
Topics cover Infile Statement, Proc import, sql pass thru, Libname, Proc access, DB Load procedure etc…
Data management:
Shapes data into a form required by the application.
Topics cover Set, Merge, Format, Informat, Update etc… statements and Functions
Data analysis:
Analyze data by using various procedures to find sum, means, STD, freq and various statistical calculations. Or transforms raw data into meaningful and useful information.
Topics cover statistical procedures to find out Sum, Means, Frequency, Univariate Anova, chi square, CMH, GLN, Regression, Correlation, STD etc. and reporting procedures like
Proc print, Report, Tabulate and _Null_ Report.
Data presentation:
How you are going to present the output to end user.
Topics covers ODS and mainly work delivery concepts
Turning Data into Information

Example:-
Data ds1;
Infile datalines;
Input id name$ sex$ age sal;
Datalines;
001 ABC M 23 50000
002 DEF F 27 45000
003 MNO F 21 70000
004 JKL F 23 44000
005 XYZ M 25 58000
;
Run;
Data ds2 (drop=age);
Set ds1;
Format sal comma6. ;
Run;
Proc sort data=ds2;
By sex;
Run;
ODS pdf file=”E:\sas\outputs\sample.pdf”;
Proc print data=ds2;
Var id name sex sal;
By sex;
Sumby sex;
Sum sal;
Run;
ODS pdf close;
Rules of SAS program
1) Every statement end with semicolon
2) Every step (both data step & proc step) end with Run statement
3) SAS Program is not case sensitive
4) Single statement can write in multiple lines or
Multiple statements can write in single line
SAS Names & Rules to write SAS Names:
SAS Program is color sensitive program, it contains
Keywords – Which are there in dark blue colour
Statements – Which are there in light blue colour
Data – Which is back ground yellow colour, or data location is in pink colour
SAS Names – Which are there in black colour
1) Names must be Less than or equal 32 character length
2) SAS Names must start with alphabetic or under score (_)
3) SAS Names should contain alphabets, numeric’s and under score (_)
But not any special characters
4) SAS Names are not case sensitive but data is case sensitive, and if it is character
Should contain single quotes.
Data types:
Character Data type:
Variable values contain letters (Alphabetic) and/or special characters.
Numeric Data type:
Variable values contain Numbers and/or Dates.
Character variable will read both character and numeric data, but numeric variable will read only numeric data.
In dataset character data is left aligned, numeric data is right aligned.
How SAS reads the data into variables
Whenever space comes in the data values or upto 8 char length in data values, whichever comes first will read to into variable.
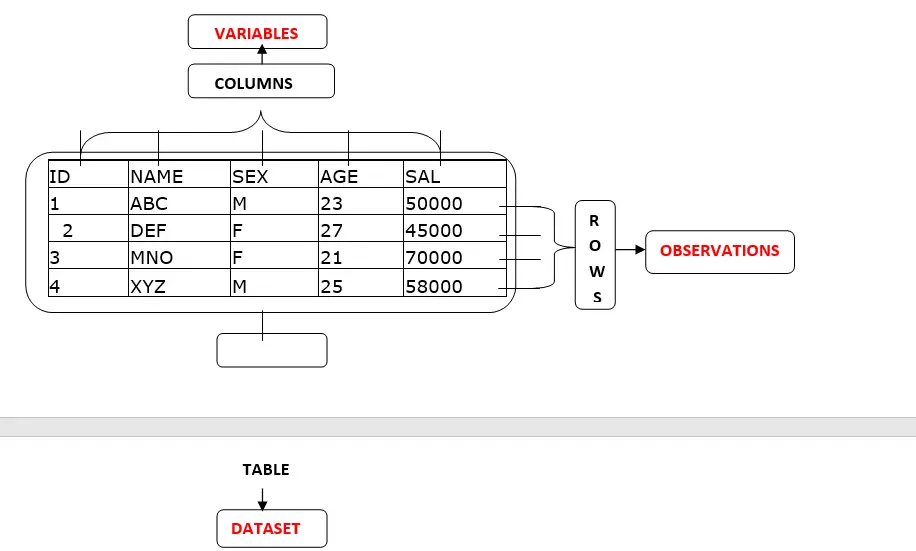
Terminology:
Tables are called datasets
Columns are called variables
Rows are called observations
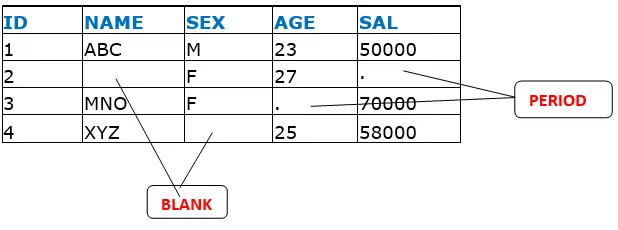
Missing Data:
The values of particular variables may be missing for some observations in that case
Missing character data represented by blanks and
Missing numeric data represented by period (.)
Example:-
Size of SAS Dataset: Prior 9.1 versions you can take maximum 32,767 columns now you can specify as many as up to your CPU memory.
We can invoke SAS in following ways
-> Interactive windowing mode (SAS windowing environment)
-> Interactive menu-driven mode (SAS Enterprise Guide,
SAS/ASSIST, SAS/AF, or SAS/EIS software etc…)
-> Batch mode
-> Noninteractive mode.
SAS Windowing Environment (Interactive windowing mode)

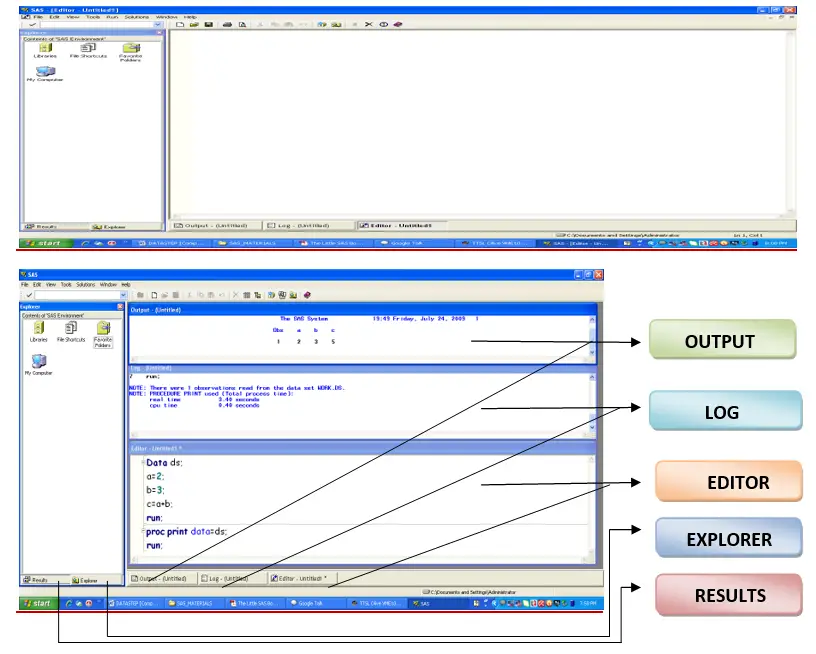
In SAS windowing environment there are 5 basic Windows
Those are (1) Editor (2) Log (3) Output (4) Explorer (5) Results
Editor Window:-
-> To write the program
-> To modify the program
-> To submit the program for execution
The default editor is the Enhanced Editor. The Enhanced Editor is syntax sensitive and color codes your programs making it easier to read them and find mistakes. The Enhanced Editor also allows you to collapse and expand the various steps in your program. For other operating environments, the default editor is the Program Editor.
Log Window:-
Log window contains information of program which submitted in Editor Window.
Generally we can get here Notes, Warnings and Errors.
How many observations are there and how many variables are there in which library datasets are storing.
Out Window
If your program generates any printable results, then it will appear in the Output window.
Explorer Window
The Explorer window gives you easy access to your SAS libraries and files.
Results Window
The Results window is like a table of contents for your Output window. The results tree lists each part of your results in an outline form.
Command Bar :-
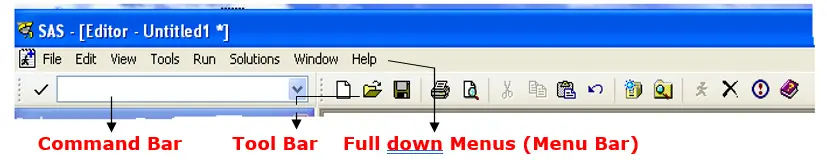
The command bar is a place that you can type in SAS commands
Most of the commands that you can type in the command bar are also accessible through the pull-down menus or the toolbar.
Example:-
X Notepad
X Time
X Date
X “E:\SAS\krishna.xls”
X “E:\SAS\IMPORT.SAS”
Tool Bar:-
Gives you quick access to commands that are already accessible through the pull-down menus.![]() (New)-
(New)-
To open New Window
The same can do thru keyboard, using Ctrl N![]() (Open) –
(Open) –
To open the program which save in server/pc location
The same can do thru keyboard, using Ctrl O![]() (Save) –
(Save) –
To save the program or Log or Output windows information in
Server location or pc location.
The same can do thru keyboard, using Ctrl S![]() (Print) –
(Print) –
To produce print of program or Log or Output windows info.
The same can do thru keyboard, using Ctrl P![]() (Print Preview) –
(Print Preview) –
Before giving the print we can check the preview of info![]() (Cut) –
(Cut) –
To cut the part of program lines in Editor Window
The same can do thru keyboard, using Ctrl X![]() (Copy)-
(Copy)-
To select the part of program lines
The same can do thru keyboard, using Ctrl C![]() (Paste) –
(Paste) –
To Paste the part of program lines
The same can do thru keyboard, using Ctrl V![]() (Undo) –
(Undo) –
To get back the part of program lines those cuts.
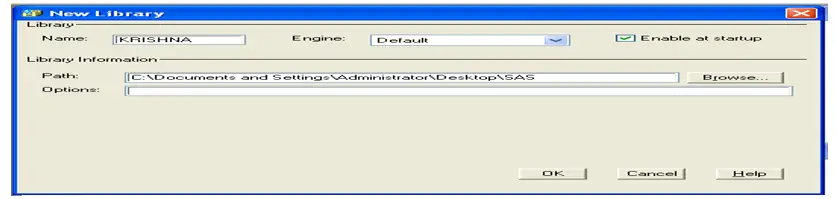
The same can do thru keyboard, using Ctrl Z![]() (New Library) –
(New Library) –
To create a new library for storing datasets Click on this icon,
Specify new library name,
Specify Engine as default,
Click enable at startup,
And browse the location where datasets should store,
And click OK.
The same can do thru keyboard, using Ctrl B
![]() (SAS Explorer)-
(SAS Explorer)-
To open SAS Explorer Window.![]() (Submit)-
(Submit)-
To submit the program for execution
This we can do in multiple ways
-> Click on this icon to execute entire SAS Session
-> Select some part of program lines and click on this icon – only selected program lines
submit for execution
-> Select some part of program lines and right click on select program lines and click
Submit selection for execute selected lines or click Submit All for execute entire SAS
Session.
-> In drill down Menus clicks Run then click submits.
-> Use F3 from keyboard.![]() (Clear All)-
(Clear All)-
To clean only Editor Window.
Other ways to clean windows
Using Ctrl E
To clean Editor Window
-> Click on above icon
-> Or right click on anywhere in Editor Window and click Clear All
-> Or in full down Menu bar click Edit then Clear All
-> Or execute below program
DM ‘EDITOR’ CLEAR;
To clean Log Window
-> Or right click on anywhere in Log Window then click on Edit
And click Clear All
-> Or in full down Menu bar click Edit then Clear All
-> Or execute below program
DM ‘LOG’ CLEAR;
To clean Output Window
-> Or right click on anywhere in output Window then click on
Edit and click Clear All
-> Or in full down Menu bar click Edit then Clear All
-> Or execute below program
DM ‘OUTPUT’ CLEAR;![]() (Break)-
(Break)-
To stop the execution program lines.
Click on this icon and select Cancel submit statements to stop the execution
Or select Terminate SAS System to close the session.![]() (Help)-
(Help)-
To get the documents and sample programs which help to learn.
Menu Bar:-
In Menu bar located at top of the window contains some full down menu’s those are
File-
-> To open new Editor Window
-> To open existing program
-> To save program
-> For print preview and
-> For Importing and Exporting data
Edit:-
-> For undo, redo, cut, copy, paste, clear all, select all,
Collapse all, expand all, find and replace
View:-
-> For getting back whichever is closed window like
Enhanced Editor, Program Editor, Log, Explorer and Output Windows
Or Write program like
DM ‘EDITOR’;
DM ‘LOG’;
DM ‘OUTPUT’;
Tools:-
-> For create new library, change font type, font size
And enable to create listing output and html output.
Run:-
-> For submitting SAS Program
And getting back last Submitted program.
Solutions:-
For analysis, Reporting
Window:-
For checking what are the windows are opened and arrange windows in software.
Help:-
To get the help from SAS documenting
SHORT CUT KEYS
Help F1
Execute F3
Recall F4
Log F6
Output F7
Zoom off F8
Short cut keys F9
Underlines First letter of Menu’s in Menu bar F10
Command Focus F11
Sub top Shift F1
Horizontal zoom Shift F3
Vertical zoom Shift F4
Zoom one on another Shift F5
Left Shift F7
Right Shift F8
Wpopup (Bring up word tip) Shift F10
Hide the current word tip ESC
Libname Ctrl B
Copy Ctrl C
Directory Ctrl D
Clear Ctrl E
Find Ctrl F
Moves line no Ctrl G
Replace Ctrl H
SAS System Options Ctrl I
Log Ctrl L
File name Ctrl Q
RFind Ctrl R
Title Ctrl T
Paste Ctrl V
Cut Ctrl X
Redo Ctrl Y
Undo Ctrl Z
Open Explorer Ctrl W
Execute the last recorded macro Ctrl F1
Move cursor to next case change ALT Right
Move cursor to previous case change ALT Left
Commenting Ctrl /
Uncommenting Ctrl Shift /
Convert the selected text to lowercase Ctrl Shift L
Convert the selected text to uppercase Ctrl Shift U
Note: Click F9 from your Keyboard to get all the shortcut keys into Log.
SAS PROGRAM
A SAS program is a sequence of statements in executed order.
SAS program having 3 components
• Data step
• Proc step
• Global options & Global statements
DATA steps are typically used to retrieve the data and create SAS data sets.
PROC steps are typically used to process SAS data sets
(That is, generate reports and graphs, edit data, and sort data).
GLOBAL OPTIONS are useful to change default settings.

Example:-
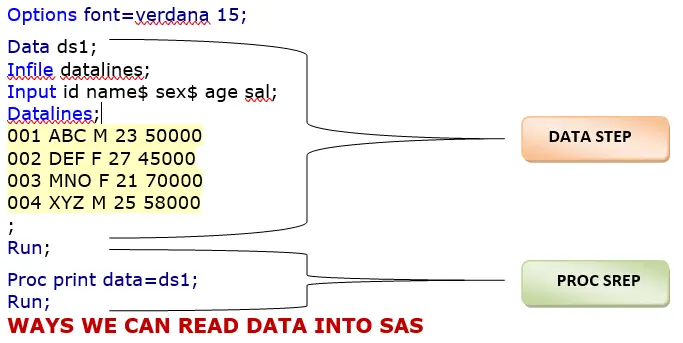
- Instream Data can enter in SAS Program itself followed by DATALINES statement
Data ds1;
Infile datalines;
Input id name$ sex$ age sal;
Datalines;
001 ABC M 23 50000
002 DEF F 27 45000
003 MNO F 21 70000
004 XYZ M 25 58000
;
Run; - Can read from External files (flat files like Notepad, Excel & csv) to SAS
Data ds;
Infile “C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator\Desktop\SAMPLE.txt”;
Input id name$ sex$ age sal;
Run;
Proc import datafile=“C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator\Desktop\SAMPLE.csv”
Out=work.ds dbms=csv replace;
Run;
Proc import datafile=“C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator\Desktop\SAMPLE.xls”
Out=work.ds dbms=excel replace;
Run;
Proc import table=demo out=work.ds dbms=access replace;
Database=“C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator\Desktop\Sample.mdb”;
Run; - Can read from existing SAS Datasets (With in SAS) to new SAS datasets.
Data work.ds;
Set sashelp.class;
Run;
- Can read from different databases to sas like Oracle DB2 Sybase etc…
Proc sql;
Connect to oracle (user=Scott password=tiger);
Create table ds3 as
Select * from connection to oracle
(
Select * from EMP
);
Disconnect from oracle;
Quit; - Can read from SAS Datasets which are located in server/pc (Out side SAS).
Libname Krishna “E:\sas”; (PC location) Libname Krishna “/sas/mis/data”; (Server location)
Libname Krishna oracle user=scott password=tiger”; (Database)
HOW THE SAS SYSTEM WORKS WITH DATA
When starts a SAS session with any mode, there is a work library this is just temporary created directory (default library) where datasets are stored for SAS session.
All the datasets are created in SAS session will be referred as Work. Prefix
Once close the session will be lost all the datasets from work Library,
If we want keep the datasets permanently need to create own library and keep the datasets permanently
How to create Library:
(Programming method)
LIBNAME Statement
Useful to create a library.
Associates a Libref with a SAS library and lists file attributes for a SAS library.
Syntax: – LIBNAME Libref ‘SAS-library’;
LIBNAME MY_SAS “E:\SAS_CLAS”;
Rules for naming a libref:
must be 8 characters or less
must begin with a letter or underscore
Remaining characters are letters, numbers, or underscores.
The specified location if already contains some SAS datasets it will reflect into New library.
Note: – If you get raw data as a SAS datasets (Not Notepads, Excel, csv & Oracle)
You can read that datasets into SAS using Libname method.
Libname My_SAS “E:/SAS/SASDATA”;
Using above program I am creating a library called My_SAS
And I specified some location to create My_SAS library so whatever SAS datasets are there in above location it will be reflect on My_SAS library.
Or
Whatever datasets you are creating in front of the dataset use your Libname so that datasets will store into your library and specified location.
Data My_SAS.ds1;
Infile datalines;
Input id name$ sex$ age sal;
Datalines;
001 abc m 23 45000
002 def f 34 67000
003 mno m 21 36000
004 xyz f 27 45000
;
Run;
(GUI method)
In Tool bar click on New Library icon and
Specify library name, Click enable at start up (To make it permanent).
And browse the location where you are going to create datasets as backup
And click ok.
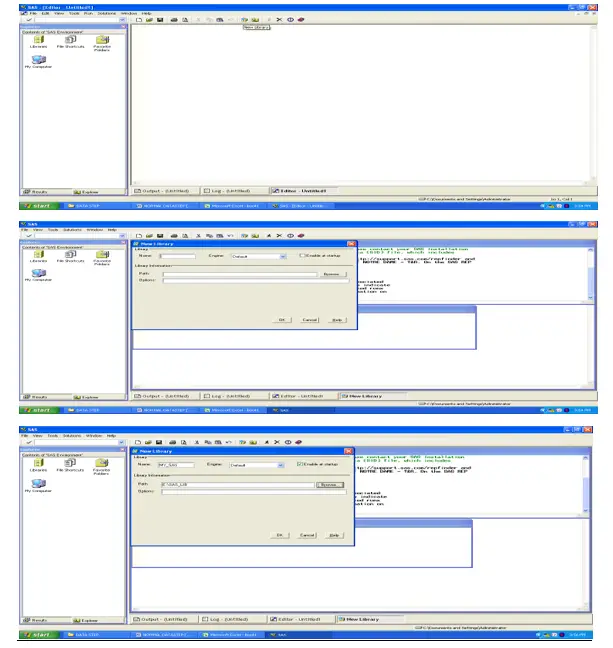
Click OK to create a Library
DATA STEP PROCESS
When the data step is submit for execution, it first undergoes a syntax check by the SAS system if no errors are found the data step is then compiled and executed .When executing the data step for instream data, the SAS system creates the following three items.
INPUT BUFFER:-
Each raw record of data is read into an area of memory when an input statement is executed.
PROGRAM DATA VECTOR:-
The SAS system builds the data set one observation at a time in this area of memory as the program is executed. values are read from the input buffer or created by programming statements and assigned to corresponding variables in the PDV. The written to a SAS data set as a single observation.
In PDV along with all variables there are 2 automatics variables those are
_ N _ and _ ERROR _
_ N_: indicates how many times the data step has iterated.
By default _ n _ =1 When iterations done its increase +1 Using we can find out how many observations are there in dataset.
_ Error _: default value =0 when error encounter it gives _ Error _ =1
If 100 of errors also _ Error _ =1 only
_ Error_ =1 is logical error it’s not a syntax error.
For Syntax error you won’t get
_error _=value. Syntax errors can see in the log with red color and wherever error is there it shows red color underline
Syntax errors are program errors and logical errors are data errors.
DESCRIPTOR INFORMATION:-
On each SAS data set, SAS creates and maintains information about data set and variable attributes like Length, Label, Format, and Informat and data type. To see this information use Proc contents procedure.
Proc contents Data=Dataset;
Run;
Example:-
Data ds;
Infile datalines;
Input id name age sex$ sal;
Datalines;
001 abc 23 m 5000
002 def 25 f 5600
003 mno 28 f 8000
004 xyz 21 m 6000
;
Run;
(Run above program and see the log for _n_ and _error_ values)
