Attributes of Variables :
Data type
Length
Label
Informat
Formats
DATATYPE
Indicates variable values are Character or Numeric data type.
If you specify $ symbol after the variable that is character data otherwise numeric data.
If you won’t specify $ symbol for character variable system thinks that is a numeric variable but contains character data so output dataset contains missing value as period.
Character variable will read both character and numeric data. But numeric variable will read only numeric data.
In dataset character data is left aligned, Numeric data is right aligned.
Example:-
Data DS;
Infile datalines;
Input id name$ sex$ age sal;
Datalines;
001 Ronald m 23 50000
002 Clark f 22 34500
003 Roopa f 26 45000
;
Run;
LENGTH STATEMENT
Specifies the number of bytes for storing variable values.
We can assign length for variables.
Syntax: – LENGTH variable(s)<$>length
Examples:-
Data DS1;
Length name $17.;
Infile datalines;
Input id name$ sex$ age sal ;
Datalines;
001 Ronaldregon m 23 50000
002 Michaleclark f 22 34500
003 Roopasubramanyam f 26 45000
;
Run;
Data ds2;
Length name $10.;
Set ds1;
Run;
Length statement always should write before Input or before Set statement or before variable. Otherwise when input executes whatever the length is there(default is 8) that will come into output.
LABEL STATEMENT
Assigns descriptive labels to variables.
Assign alias names to variables.
Label can’t change the column name permanently like rename
Syntax: – LABEL variable-1=’label-1′ . . . <variable-n=’label-n’>;
LABEL variable-1=’ ‘ . . . <variable-n=’ ‘>;
Data DS1;
Infile datalines;
Input id name$ sex$ age sal;
Label name=’Emp Name’ sex=’Gender’ sal=’Income’;
Datalines;
001 Ronald m 23 50000
002 Clark f 22 34500
003 Roopa f 26 45000
;
Run;
Data DS2;
Infile datalines;
Label name=’Emp Name’ sex=’Gender’ sal=’Income’;
Input id name$ sex$ age sal;
Datalines;
001 Ronald m 23 50000
002 Clark f 22 34500
003 Roopa f 26 45000
;
Run;
If we write Label statement after input statement output dataset will be in input order
But if we write before input, output dataset order should be in label order then what ever variable is not there in label those will come in input order
If we specify label is ‘ ‘ raw data variable name should come into output dataset.
Means below example Label name=’ ‘ so output dataset contains existing variable is name
Data DS3;
Infile datalines;
Input id name$ sex$ age sal;
Label name=’ ‘ sex=’Gender’ sal=’ ‘;
Datalines;
001 Ronald m 23 50000
002 Clark f 22 34500
003 Roopa f 26 45000
;
Run;
INFORMAT STATEMENT
Informat is an instruction that SAS uses to read data values into a variable.
Informats are usually specified in an input statement. If coded with the informat statements, attach an informat to a variable for subsequent input.
Informats can be user-written Informats also.
Syntax: – INFORMAT variable-1<informat-1> variable-N<informat-N>;
Categories of Informats:-
1. Character Informats
2. Numeric Informats
3. Date, Time, Datetime Informats
4. Column binary Informats
5. User defined Informats
Character Informats: –
Reads character data into character variables.
Syntax: – $informatw.
Ex: – $
$10.
$20.
$Char.
Examples:-
Data infmt6;
Input id name$ age sex$ sal;
Datalines;
001 David 23 m 50000
002 Amelia 32 f 25000
003 Alan 31 f 30000
004 Ravi 21 m 45000
005 Jim 35 f 28000
;
Run;
Data informat6a;
Input idno name & $18. team$ strtwght endwght;
Datalines;
1023 David Shaw red 189 165
1049 Amelia Serrano yellow 145 124
1219 Alan Nance red 210 192
1246 Ravi Sinha yellow 194 177
1078 Ashley McKnight red 127 118
1221 Jim Brown yellow 220 .
;
Run;
Numeric Informats: –
Reads numeric data values from numeric variables
Syntax: – informatw.d
Ex: – Comma12. Dollar10.2
Examples:-
Data infmt1;
Infile datalines;
Input id name$ age sex$ sal;
Datalines;
001 David 23 m 50000
002 Amelia 32 f 25000
003 Alan 31 f 30000
004 Ravi 21 m 45000
005 Jim 35 f 28000
;
Run;
In above example data and columns are same data type so you can read. But see below program sal values are containing special character but sal variable is numeric so you can’t read data in this case we can specify informat to read data, not only with comma when numeric data contains special characters like comma, dollar, euro we can specify Numeric Informats like below.
Data infmt2;
Infile datalines;
Input id name$ age sex$ sal comma6.;
Datalines;
001 David 23 m 50,000
002 Amelia 32 f 25,000
003 Alan 31 f 30,000
004 Ravi 21 m 45,000
005 Jim 35 f 28,000
;
Run
Data infmt3;
Infile datalines;
Input id name$ age sex$ sal;
Informat sal comma6. ;
Datalines;
001 David 23 m 50,000
002 Amelia 32 f 25,000
003 Alan 31 f 30,000
004 Ravi 21 m 45,000
005 Jim 35 f 28,000
Run;
Data infmt4;
Infile datalines;
Input id name$ age sex$ sal dollar5. ;
Datalines;
001 David 23 m $5000
002 Amelia 32 f $2500
003 Alan 31 f $3000
004 Ravi 21 m $4500
005 Jim 35 f $28000
;
Run;
Data infmt5;
Infile datalines; Informat we can write with Input
Input id name$ age sex$ sal dollar6. ; statement after the variable or we can
/*Informat sal dollar6. ;*/ write as a separate statement like this
Datalines;
001 David 23 m $5,000
002 Amelia 32 f $2,500
003 Alan 31 f $3,000
004 Ravi 21 m $4,500
005 Jim 35 f $2,800
;
Run;
Data infmt6;
Infile datalines;
Input id name$ age sex$ sal dollar9.2 ;
Format sal dollar10.2;
Datalines;
001 David 23 m $50000.55
002 Amelia 32 f $25000.00
003 Alan 31 f $30000.05
004 Ravi 21 m $45000.07
005 Jim 35 f $28000.99
;
Run;
Date and time Informats:-
Reads data values into variables representing time, dates and date times.
Syntax: – informatw.
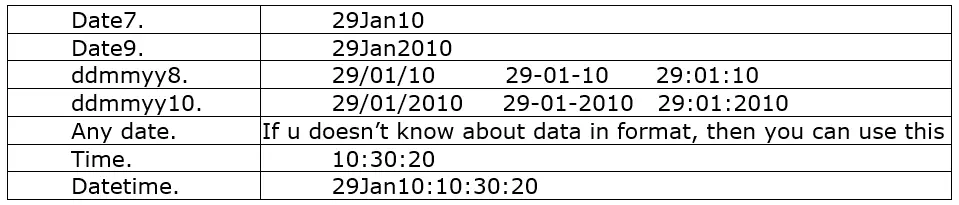
Examples:-
Data infmt7;
Infile datalines;
Input id name$ age sex$ sal dob;
Datalines;
001 David 23 m 50000 10Feb1983
002 Amelia 32 f 25000 15May1984
003 Alan 31 f 30000 21Jul1984
004 Ravi 21 m 45000 05Aug1984
005 Jim 35 f 28000 30Jan1985
;
Run;
In SAS dates are Numeric data type but DOB values contains character values in above example, so we can’t read, to read dates we should use date informats like below
Data infmt7a;
Infile datalines;
Input id name$ age sex$ sal dob date9.;
/*Informat dob date9.;*/
Datalines;
001 David 23 m 50000 10Feb1983
002 Amelia 32 f 25000 15May1984
003 Alan 31 f 30000 21Jul1984
004 Ravi 21 m 45000 05Aug1984
005 Jim 35 f 28000 30Jan1985
;
Run;
Data infmt7b;
Infile datalines;
Input id name$ age sex$ sal dob date7.;
/*Informat dob date7.;*/
Datalines;
001 David 23 m 50000 10Feb83
002 Amelia 32 f 25000 15May84
003 Alan 31 f 30000 21Jul84
004 Ravi 21 m 45000 05Aug84
005 Jim 35 f 28000 30Jan85
;
Run;
Data infmt7c;
Infile datalines;
Input id name$ age sex$ sal dob anydtdte.;
/*Informat dob date9.;*/
Datalines;
001 David 23 m 50000 10Feb1983
002 Amelia 32 f 25000 15May1984
003 Alan 31 f 30000 21Jul1984
004 Ravi 21 m 45000 05Aug1984
005 Jim 35 f 28000 30Jan1985
;
Run;
Data infmt8;
Infile datalines;
Input id name$ age sex$ sal dob date9. doj:ddmmyy10. ;
/*Input id name$ age sex$ sal dob anydtdte9. doj:anydtdte10.;*/
Datalines;
001 David 23 m 50000 10Feb1983 12/01/2011
002 Amelia 32 f 25000 15May1984 15/01/2011
003 Alan 31 f 30000 21Jul1984 31/01/2011
004 Ravi 21 m 45000 05Aug1984 25/02/2011
005 Jim 35 f 28000 30Jan1985 08/03/2011
;
Run;
Data infmt8a;
Infile datalines;
Input id name$ age sex$ sal dob date9. doj:ddmmyy8. ;
/*Informat dob date9. doj ddmmyy8.;*/
Datalines;
001 David 23 m 50000 10Feb1983 12/01/11
002 Amelia 32 f 25000 15May1984 15/01/11
003 Alan 31 f 30000 21Jul1984 31/01/11
004 Ravi 21 m 45000 05Aug1984 25/02/11
005 Jim 35 f 28000 30Jan1985 08/03/11
;
Run;
Data infmt8b;
Infile datalines;
Input id name$ age sex$ sal dob doj;
Informat dob date9. doj ddmmyy10.;
Datalines;
001 David 23 m 50000 10Feb1983 12/01/2011
002 Amelia 32 f 25000 15May1984 15/01/2011
003 Alan 31 f 30000 21Jul1984 31/01/2011
004 Ravi 21 m 45000 05Aug1984 25/02/2011
005 Jim 35 f 28000 30Jan1985 08/03/2011
;
Run;
Data infmt9;
Infile datalines;
Input id name$ age sex$ sal dob datetime.;
Datalines;
001 David 23 m 50000 10Feb1983:10:30:15
002 Amelia 32 f 25000 15May1984:11:23:23
003 Alan 31 f 30000 21Jul1984:08:34:45
004 Ravi 21 m 45000 05Aug1984:12:43:56
005 Jim 35 f 28000 30Jan1985:03:35:12
;
Run;
Data infmt9a;
Input id name$ age sex$ sal dob ;
Informat dob time.;
Datalines;
001 David 23 m 50000 10:30:15
002 Amelia 32 f 25000 11:23:23
003 Alan 31 f 30000 08:34:45
004 Ravi 21 m 45000 12:43:56
005 Jim 35 f 28000 03:35:12
;
Run;
Column binary Informats:-
Reads data stored in column- binary or multi –punched form into character and numeric variables
Ex: – row 12.3, $ cd4.
User defined Informats:-
Created by using proc format.
Programmer can create his own informats to read the data using Proc Format.
FORMAT STATEMENT
Format is an instruction that SAS uses to write data values.
The format is exactly the same as that for informat.
Infact most SAS defined informats are also SAS defined formats.
However there are some informats such as anydtdte.
That is not defined as Format
Syntax: – FORMAT variable-1<format-1> variable-N<format-N>;
Categories of Formats:-
1. Character Formats
2. Numeric Formats
3. Date, Time, Datetime Formats
4. Column binary Formats
5. User defined Formats
Character Formats: –
Writes character data values from character variables
Character informats and character formats both are same
Syntax: – $ formatw.
Ex: – $
$10.
$20.
$char10.
Examples:-
Data fmt5;
Infile datalines;
Input id name$ age sex$ sal;
Datalines;
001 David 23 m 50000
002 Amelia 32 f 25000
003 Alan 31 f 30000
004 Ravi 21 m 45000
005 Jim 35 f 28000
;
Run;
Data fmt5a;
Infile datalines;
Input idno name & $18. team$ strtwght endwght;
Datalines;
1023 David Shaw red 189 165
1049 Amelia Serrano yellow 145 124
1219 Alan Nance red 210 192
1246 Ravi Sinha yellow 194 177
1078 Ashley McKnight red 127 118
1221 Jim Brown yellow 220 .
;
Run;
Numeric Formats: –
Writes numeric data values from numeric variables.
Syntax: – formatw.d
Ex: – Dollar10.
Dollar 10.2
Comma10.
Comma10.2
Percent 4.2
Best10.
Examples:-
Data fmt1;
Infile datalines;
Input id name$ age sex$ sal comma6.;
Format sal comma6.;
/*Format sal comma9.2;*/
Datalines;
001 David 23 m 50,000
002 Amelia 32 f 25,000
003 Alan 31 f 30,000
004 Ravi 21 m 45,000
005 Jim 35 f 28,000
;
Run;
Data fmt2;
Infile datalines;
Input id name$ age sex$ sal;
Informat sal comma9.2;
Format sal comma9.2;
Datalines;
001 David 23 m 50,000.55
002 Amelia 32 f 25,000.00
003 Alan 31 f 30,000.60
004 Ravi 21 m 45,000.77
005 Jim 35 f 28,000.50
;
Run;
Data fmt3;
Infile datalines;
Input id name$ age sex$ sal dollar5. ;
Format sal dollar5.;
Datalines;
001 David 23 m $5000
002 Amelia 32 f $2500
003 Alan 31 f $3000
004 Ravi 21 m $4500
005 Jim 35 f $28000
;
Run;
Data fmt3a;
Infile datalines;
Input id name$ age sex$ sal dollar6. ;
/*Format sal dollar6.;*/
Format sal dollar9.2;
/*Format sal comma6.;*/
Datalines;
001 David 23 m $5,000
002 Amelia 32 f $2,500
003 Alan 31 f $3,000
004 Ravi 21 m $4,500
005 Jim 35 f $2,000
;
Run;
Date, Time and Datetime Formats: –
Write data values from variables representing Time, date and date time variables.
Syntax: – formatw.
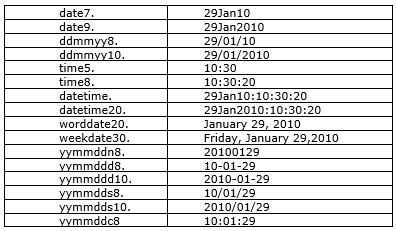
Examples:-
Data fmt6;
Infile datalines;
Input id name$ age sex$ sal dob date9.;
Format dob date9.;
/*Format dob date7.;*/
/*Format dob date9.;*/
/*Format dob ddmmyy8.;*/
/*Format dob ddmmyy10.;*/
/*Format dob worddate20.;*/
/*Format dob weekdate30.;*/
/*Format dob yymmddN8.;*/
/*Format dob yymmddS8.;*/
/*Format dob yymmddS10.;*/
/*Format dob yymmddD8.;*/
/*Format dob yymmddD10.;*/
/*Format dob yymmddC8.;*/
/*Format dob yymmddC10.;*/
Datalines;
001 David 23 m 50000 10Feb1983
002 Amelia 32 f 25000 15May1984
003 Alan 31 f 30000 21Jul1984
004 Ravi 21 m 45000 05Aug1984
005 Jim 35 f 28000 30Jan1985
;
Run;
Data fmt7;
Infile datalines;
Input id name$ age sex$ sal dob date9. doj:ddmmyy10. ;
Format dob worddate20. doj weekdate30.;
Datalines;
001 David 23 m 50000 10Feb1983 12/01/2011
002 Amelia 32 f 25000 15May1984 15/01/2011
003 Alan 31 f 30000 21Jul1984 31/01/2011
004 Ravi 21 m 45000 05Aug1984 25/02/2011
005 Jim 35 f 28000 30Jan1985 08/03/2011
;
Run;
Data fmt8;
Infile datalines;
Input id name$ age sex$ sal dob ;
Informat dob datetime.;
Format dob datetime.;
/*Format dob datetime20.;*/
Datalines;
001 David 23 m 50000 10Feb1983:10:30:15
002 Amelia 32 f 25000 15May1984:11:23:23
003 Alan 31 f 30000 21Jul1984:08:34:45
004 Ravi 21 m 45000 05Aug1984:12:43:56
005 Jim 35 f 28000 30Jan1985:03:35:12
;
Run;
Data fmt9;
Infile datalines;
Input id name$ age sex$ sal dob ;
Informat dob time.;
Format dob time.;
/*Format dob time8.;*/
/*Format dob time5.;*/
Datalines;
001 David 23 m 50000 10:30:15
002 Amelia 32 f 25000 11:23:23
003 Alan 31 f 30000 08:34:45
004 Ravi 21 m 45000 12:43:56
005 Jim 35 f 28000 03:35:12
;
Run;
Column binary Formats: –
Writes data stored in column- binary or multi –punched form into character and numeric variables.
Ex: – row 12.3 $cd4.
User defined Formats: –
Created by using proc format.
(This topic covers in deeply in Proc Format)
Examples:-
Data fmt9a;
Infile datalines;
Input id name$ age sex$ sal dob time.;
Format dob time.;
Datalines;
001 David 23 m 50000 10:30:15
002 Amelia 32 f 25000 11:23:23
003 Alan 31 f 30000 08:34:45
004 Ravi 21 m 45000 12:43:56
005 Jim 35 f 28000 03:35:12
;
Run;
Proc format;
Value $gen ‘f’=’Female’ ‘m’=’Male’;
Run;
Applying Format in Dataset
Data fmt9b;
Set fmt9a;
Format sex $gen.;
Run;
Applying Format in Report
Proc report data=fmt9a nowd;
Column id name age sex sal dob ;
Define Sex/display format=$gen.;
Run;
Applying Format in Report with styles
Proc format;
Value $col ‘f’=’RED’ ‘m’=’GREEN’;
Run;
Proc sort data=fmt9a;
By sex;
Run;
Proc print data=fmt9a NOOBS;
VAR id name age sal dob sex/style=[background=$col.] ;
Id sex;
By sex;
Sumby sex;
Sum sal;
RUN;
Note: we can specify attributes as individually with above statements like Length, Label, Informat and Format or all attributes we can specify with one statement that is Attrib Statement.
ATTRIB STATEMENT
Associates a format, informat, label, and/or length with one or more variables
Syntax: – ATTRIB variable-list(s) attribute-list(s) ;
Generally using Attrib statement we can change length, format, informat and label.
Data DS1;
Attrib name length=$10.;
Input id name$ sex$ age sal ;
Datalines;
001 Ronald m 23 50000
002 Clark f 22 34500
003 Roopa f 26 45000
;
Run;
Data DS2;
Attrib name length=$10. label=’Emp Name’;
Input id name$ sex$ age sal;
Datalines;
001 Ronald m 23 50000
002 Clark f 22 34500
003 Roopa f 26 45000
;
Run;
Data DS3;
Attrib name length=$10. label=’Emp name’
sal format=comma6. label=’Income’;
Input id name$ sex$ age sal;
Datalines;
001 Ronald m 23 50000
002 Clark f 22 34500
003 Roopa f 26 4500
;
Run;
Data DS4;
Attrib name length=$10.
doj format=worddate30. Label=’Date of joining’
sex label=’gender’ sal format=dollar7. ;
Input id name$ sex$ age sal doj date9.;
Datalines;
001 Ronald m 23 50000 02Jan2009
002 Clark f 22 34500 22Feb2010
003 Roopa f 26 45000 30Apr2010
;
Run;
Data DS5;
Attrib name length=$10.
dob informat=date9. format=ddmmyy8. Label=’Date of Birth’
doj informat=anydtdte9. format=ddmmyy10. Label=’Date of Joining’
sex label=’gender’
sal format=dollar7. ;
Infile datalines;
Input id name$ sex$ age sal dob doj ;
Datalines;
001 Ronald m 23 50000 11Mar1986 02Jan2009
002 Clark f 22 34500 30Dec1986 22Feb2010
003 Roopa f 26 45000 06Aug1987 30Apr2010
;
Run;
Data DS6;
Infile datalines;
Input id name$ sex$ age sal dob doj ;
Attrib name label=’Empname’
dob informat=date9. format=ddmmyy8. Label=’Date of Birth’
doj informat=anydtdte9. format=ddmmyy10. Label=’Date of Joining’
sex label=’gender’
sal format=dollar7. ;
Datalines;
001 Ronald m 23 50000 11Mar1986 02Jan2009
002 Clark f 22 34500 30Dec1986 22Feb2010
003 Roopa f 26 45000 06Aug1987 30Apr2010
;
Run;
Data DS7;
Infile datalines;
Input id name$ sex$ age sal dob date9. doj:date9. ;
Datalines;
001 Ronald m 23 50000 11Mar1986 02Jan2009
002 Clark f 22 34500 30Dec1986 22Feb2010
003 Roopa f 26 45000 06Aug1987 30Apr2010
;
Run;
Data DS7a;
Attrib name length=$10.
dob informat=date9. format=ddmmyy8. Label=’Date of Birth’
doj informat=anydtdte9. format=ddmmyy10. Label=’Date of Joining’
sex label=’gender’
sal format=dollar7. ;
Set DS6;
Run;
Note: When we specify length as an attribute with Attrib statement, Attrib statement must write before Input or before Set statement otherwise when input statement or set statement executes whatever the length is there for variable that will come into output.
And the output dataset variable order also change accordingly attrib statement variables order that we can change again into required order in Proc print
But if we specify Attrib statement after Input or Set statement dataset order is Input statement order (we can specify like this when we are not using Length in attrib statement).
