Conditional Statements :
IF Statement, Subsetting
Continues processing only those observations that meet the condition.
Syntax: – IF expression;
Examples:-
Data ds1;
Input idno name $ team $ strtwght endwght;
Cards;
1023 David red 189 165
1049 Amelia yellow 145 124
1219 Alan red 210 192
1246 Ravi yellow 194 177
1078 Ashley red 127 118
1221 Jim yellow 220 .
;
Run;
Data ds2;
Set ds1;
If team=’red’;
Run;
Data subset;
Set sashelp.class;
If sex=’F’;
/*If age > 12;*/
Run;
IF-THEN Statement
Executes a SAS statement for observations that meet specific conditions
And it is useful to rename data values.
Syntax: – IF expression THEN statement;
Data ds3;
Set ds1;
If team=’red’ then team=1;
Run;
Data ds3a;
Set ds1;
If team=’red’ then team=1;
If team=’yellow’ then team=2;
If team=’green’ then team=3;
If team=’blue’ then team=4;
Run;
Data ds3b;
Set ds1;
If team=’red’ then team=’R’;
If team=’yellow’ then team=’Y’;
If team=’green’ then team=’G’;
If team=’blue’ then team=’B’;
Run;
Data ds3c;
Set ds1;
If team=’red’ then team1=’R’;
If team=’yellow’ then team1=’Y’;
If team=’green’ then team1=’G’;
If team=’blue’ then team1=’B’;
Run;
Data ds;
Length sex $6.;
Set sashelp.class;
If sex=’F’ then sex=’Female’;
If sex=’M’ then sex=’Male’;
Run;
Data ds;
Length gender $6.;
Set sashelp.class;
If sex=’M’ then gender=’Male’;
If sex=’F’ then gender=’Female’;
Run;
IF-THEN/ELSE Statement
Executes a SAS statement for observations that meet specific conditions and it is useful to rename data values with less execution time compare with If–Then statement.
Syntax: – IF expression THEN statement; <ELSE statement ;>
Data ds4 ;
Set ds1;
If team=’red’ then team=1;
Else team=2;
Run;
Data ds4a ;
Set ds1;
If team=’red’ then team=1;
Else if team=’yellow’ then team=2;
Else if team=’green’ then team=3;
Else team=4;
Run;
Data ds;
Length sex $6.;
Set sashelp.class;
If sex=’M’ then sex=’Male’; Else sex=’Female’;
Run;
Data ds;
Length gender $6.;
Set sashelp.class;
If sex=’M’ then gender=’Male’; Else gender=’Female’;
Run;
IF-THEN/ELSE OUTPUT
Executes a SAS statement for observations that meet specific conditions
Using this we can create multiple datasets at a time based on conditions.
Syntax:- IF expression THEN OUTPUT; <ELSE OUTPUT>;
Data ds5 ds6 ;
Set ds1;
If team=’red’ then output ds5;
Else output ds6;
Run;
Data ds5 ds6 ds7 ds8;
Set ds1;
If team=’red’ then output ds5;
Else if team=’yellow’ then output ds6;
Else if team=’green’ then output ds7;
Else output ds8;
Run;
Data ds9 ds10;
Set sashelp.class;
If sex=’M’ then output ds9;
Else output ds10;
Run;
IF-THEN DELETE
Executes a SAS statement for observations that meet specific conditions
Using this we can delete observations based on condition
Syntax: – IF expression THEN DELETE;
Data ds9;
Set ds1;
If team=’red’ then delete;
Run;
Data ds9 ds10;
Set ds1;
If team=’red’ then delete;
Else output ds10;
Run;
IF-THEN REMOVE
Delete observations when it meets condition
Syntax: – IF expression THEN REMOVE;
Data ds;
Set sashelp.class;
Run;
Data ds;
Modify ds;
If age=12 then remove;
Run;
IF-THEN DO
Giving order to do when it meet condition.
Syntax: – IF expression THEN DO;
Data ds;
Set sashelp.class;
If sex=’F’ then do; x=1; End;
Else do; x=2; End;
Run;
WHERE Statement
Selects observations from SAS data sets that meet a particular condition.
Syntax:-
Where expression;
where-expression-1 < logical-operator where-expression-n>;
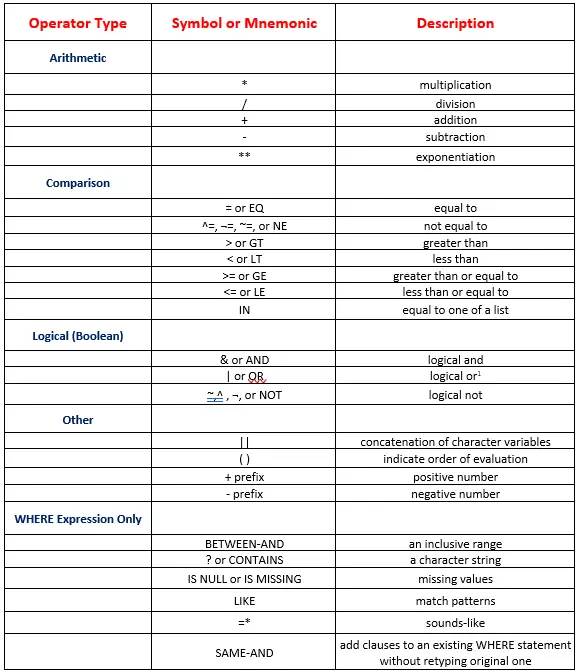
Examples:-
Data ds1;
Input pid drug$ visit_date date9.;
Format visit_date date9.;
Cards;
101 asp-05mg 12jan2005
102 asp-10mg 14jan2005
101 asp-05mg 18jan2005
101 asp-05mg 21jan2005
103 asp-15mg 12jan2005
101 asp-05mg 30jan2005
101 asp-05mg 23jan2005
102 asp-10mg 12jan2005
101 asp-05mg 11jan2005
103 asp-15mg 12jan2005
101 asp-05mg 15jan2005
104 asp-20mg 12jan2005
101 asp-05mg 16jan2005
102 asp-10mg 12jan2005
103 asp-15mg 12jan2005
103 asp-15mg 12jan2005
101 asp-05mg 15jan2005
;
Run;
Data ds2;
Set ds1;
Where pid=101;
Run;
Data ds2;
Set ds1;
Where pid ne 103;
Run;
Data ds2a;
Set ds1;
Where pid>101;
Run;
Data ds2a;
Set ds1;
Where pid>=101;
Run;
Data ds2b;
Set ds1;
Where drug=’asp-10mg’;
Run;
Data ds2c;
Set ds1;
Where date=’15jan2005’d;
Run;
Where with few Operators & expressions
WHERE AND
Data ds3a;
Set ds1;
where visit_date >’12jan2005’d and visit_date <’21jan2005’d ;
Run;
Data ds3b;
Set ds1;
Where pid >101 and pid <104 ;
Run;
WHERE BETWEEN
Data ds4;
Set ds1;
Where visit_date between ’15jan2005’d and ’21jan2005’d ;
Run;
Data ds3b;
Set ds1;
Where pid between 101 and 104 ;
Run;
WHERE SAME AND
data ds1a;
set ds1;
where visit_date > ’12jan2005’d;
where same and visit_date < ’21jan2005’d;
Run;
It works like where and operator.
All above 3 operators (AND, BETWEEN, SAME AND) are useful to select observations between two expressions.
WHERE IN
When you have multiple values in condition while selecting observations.
Data ds5;
Set ds1;
where pid in (102, 103 ) ;
Run;
WHERE NOT IN
Data ds5;
Set ds1;
where pid not in (102, 103 ) ;
Run;
WHERE LIKE
Like operator is useful to select the observations with particular position of letter in a variable value.
Data ds6;
Input p_id drug_name$ visit_date date9.;
Format visit_date date9.;
Cards;
101 asp-05mg 12jan2005
102 asp-10mg 14jan2005
101 bsp-05mg 18jan2005
102 aap-10mg 12jan2005
101 csp-05mg 21jan2005
103 amp-15mg 12jan2005
101 dsp-05mg 30jan2005
102 dsp-10mg 12jan2005
;
Run;
Data ds6a;
Set ds6;
Where drug_name like ‘c%’ ;
Run;
Data ds6b;
Set ds6;
Where drug_name like ‘_a%’ ;
Run;
Data ds6c;
Set ds6;
Where drug_name like ‘_____5%’ ;
Run;
Data ds6d;
Set ds6;
Where drug_name like ‘%g’ ;
Run;
Data ds6e;
Set ds6;
Where drug_name like ‘%m_’ ;
Run;
Data ds6f;
Set ds6;
Where drug_name like ‘%0__’ ;
Run;
Data ds6g;
Set ds6;
Where drug_name like ‘asp%’ ;
Run;
Data ds6h;
Set ds6;
Where drug_name like ‘%a%’ ;
Run;
WHERE CONTAINS(?)
Select the data where ever that letter is there in variable
But letter is case sensitive.
Data ds1;
Length name $12.;
Input name$ sex$ sal dollar5.;
Format sal dollar6.;
Datalines;
Ramakrishna m $5000
pragna f $3500
Raju m $4500
Mohanprasad m $6000
;
Run;
Data ds2;
Set ds1;
Where name contains ‘r’;
Run;
Data ds3;
Set ds1;
Where name contains ‘R’;
Run;
Data ds4;
Set ds1;
Where name ? ‘R’;
Run;
WHERE NULL/MISSING
Select observations when it contains missing value.
Data ds1;
Input p_id 3. +1 drug_name$8. +1 visit_date date9.;
Format visit_date date9.;
Cards;
101 asp-05mg 12jan2005
102 asp-10mg 14jan2005
101 bsp-05mg 18jan2005
102 12jan2005
101 csp-05mg 21jan2005
103 amp-15mg 12jan2005
101 30jan2005
102 dsp-10mg 12jan2005
;
Run;
Data ds1a;
Set ds1;
where drug_name is null;
Run;
Data ds1b;
Set ds1;
where drug_name is missing;
Run;
WHERE SOUNDS-LIKE
Select the data only when sound is same .
Even spelling is different also it will pick observations if pronunciation is same.
Data ds1;
Input p_id p_name$ drug_name$ visit_date date9.;
Format visit_date date9.;
Cards;
101 john asp-05mg 12jan2005
102 smith asp-10mg 14jan2005
101 smit bsp-05mg 18jan2005
102 clark aap-10mg 12jan2005
101 manish csp-05mg 21jan2005
103 clarc amp-15mg 12jan2005
101 ronald dsp-05mg 30jan2005
102 ronold dsp-10mg 12jan2005i
;
Run;
Data ds1a;
Set ds1;
where p_name=’smith’;
Run;
Data ds1b;
Set ds1;
where p_name=*’smith’;
Run;
Difference between IF and WHERE Statement
1) IF works in only data step (Except in proc report it works with compute statement) .
But where works in both data step and proc step.
2) IF we can use while reading the data from Datalines, External files & existing dataset.
But where we can use only when we are reading from existing dataset.
3) IF works with arithmetic operators, logical operators, comparison operators but can’t
work with expressions. But where works with arithmetic operators, logical operators,
comparison operators and expressions also.
4) IF works after pdv
But where works before pdv.
So where is efficient then If why because it reduce execution time.
