Proc Import :
PROC IMPORT reads data from an external data source and writes it to a
SAS data set. External source should be Excel sheets, CSV, Access files etc…
PROC IMPORT reads data from an external data source and writes it to a SAS data set.
Base SAS can import delimited files. In delimited files, a delimiter–such as a blank, comma,
or tab–separates columns of data values. If you have license for SAS/ACCESS Interface
to PC Files, additional external data sources can include such files as
Microsoft Access Database, Excel files, and Lotus spreadsheets.
Syntax:-
PROC IMPORT DATAFILE=”RAWDATALOCATION”
OUT=LIBREF.DATASET
DBMS=SOURCE IDENTIFIER
REPLACE;
GETNAMES=YES|NO;
DATAROW=RECORDNO;
GUESSINGROWS=NO OF ROWS
SHEET=”SHEET_NAME”
RUN;
Examples:-
Datafile=”File location”
Specifies the complete path and filename.ext of the input PC file, spreadsheet, or delimited external file. If the name does not include special characters (such as the backslash in a path), lowercase characters, or spaces, you can omit the quotes.
OUT=SAS-data-set
Identifies the output SAS data set with either a one- or two-level SAS name (library and member name). If the specified SAS data set does not exist, PROC IMPORT creates it. If you specify a one-level name, PROC IMPORT uses the WORK library.
TABLE=”tablename”
Specifies the table name of the input DBMS table. If the name does not include special characters (such as question marks), lowercase characters, or spaces, you can omit the quotes. Note that the DBMS table name may be case-sensitive.
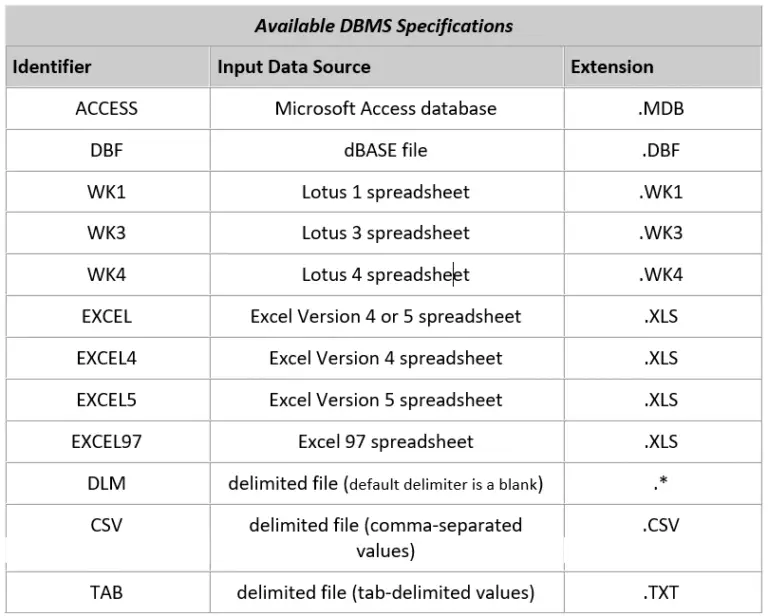
DBMS=identifier
Specifies the type of data to import. For example, DBMS=DBF specifies to import a dBASE file. For PC files, spreadsheets, and delimited external files, you do not have to specify DBMS= if the filename specified with DATAFILE= contains a valid extension so that PROC IMPORT can recognize the type of data. For example, PROC IMPORT recognizes the filename ACCOUNTS.WK1 as a Lotus 1 spreadsheet and the filename MYDATA.CSV as a delimited external file that contains comma-separated data values. PROC IMPORT can recognize the difference between Excel Version 4 and Version 5 spreadsheets when you use the extension .XLS, regardless of whether you specify DBMS=EXCEL, DBMS=EXCEL4, or DBMS=EXCEL5. However, you must specify DBMS=EXCEL97 to import Excel 97 spreadsheets. If you do not specify an identifier or if the extension of the filename is not recognized, an error is returned.
To import a DBMS table, you must specify DBMS= using a valid database product. For example, DBMS=ACCESS imports a Microsoft Access table.
The DBMS= specification can include the values listed in the following table:
REPLACE
Overwrites an existing SAS data set. If you do not specify REPLACE, PROC IMPORT does not overwrite an existing data set.
DATAROW=1 to 32767
Starts reading data from the specified row number in the delimited text file.
When GETNAMES=NO, DATAROW must be equal to or greater than 1.
When GETNAMES=YES, DATAROW must be equal to or greater than 2.
DELIMITER
Specifies the delimiter that separates columns of data in the input file. You can specify the delimiter as a single character or as a hexadecimal value. For example, if columns of data are separated by an ampersand, specify DELIMITER=’&’. If you do not specify DELIMITER=, the IMPORT procedure assumes that the delimiter is a space.
Valid values are anychar|nn|x|space.
GETNAMES=YES/NO
Specifies whether the IMPORT procedure generate SAS variable names from the data values in the first record in the input file.
GUESSINGROWS=
Specifies the number of rows of the file to scan to determine the appropriate data type and length for the columns. The scan data process scans from row 1 to the number that is specified by the GUESSINGROWS option.
Default rows=20
Valid values is 1 to 32767
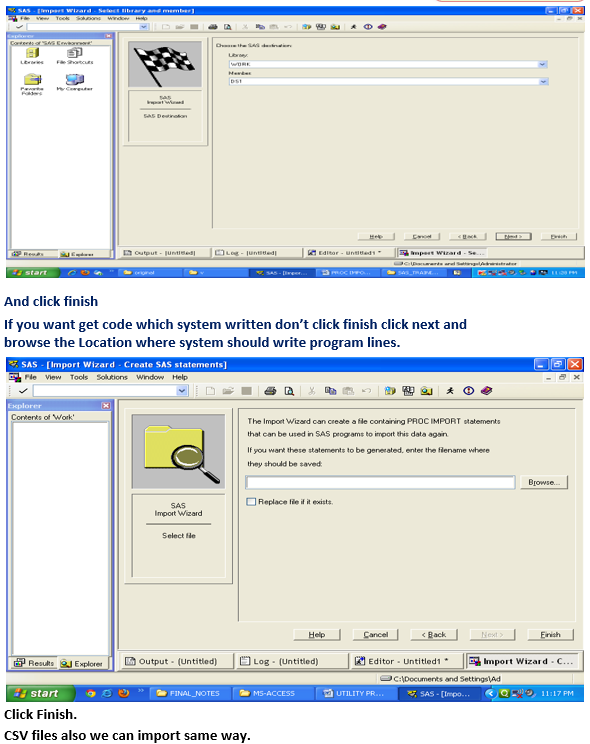
To import data, you can also use the Import Wizard
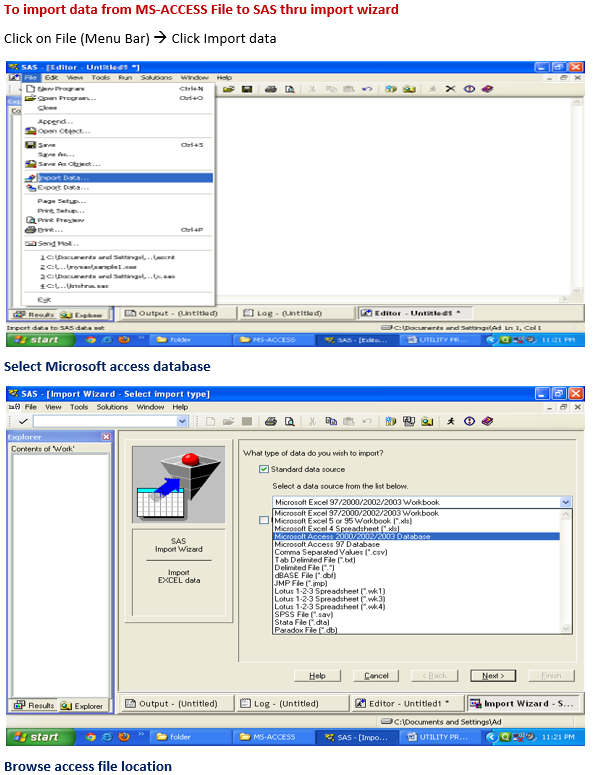
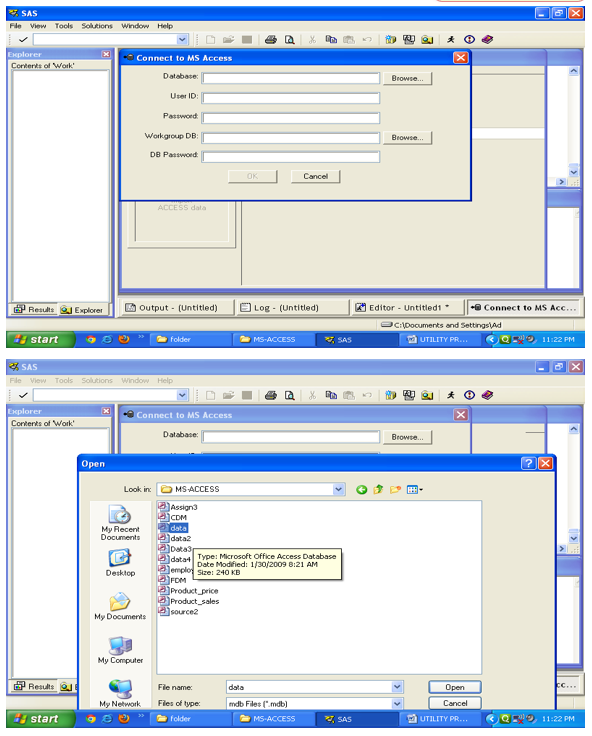
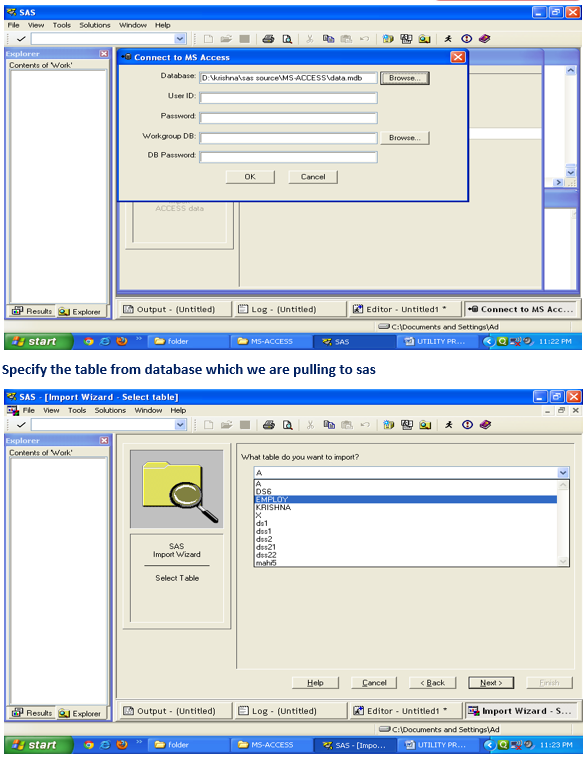
To import data from MS-Excel File to SAS thru import wizard
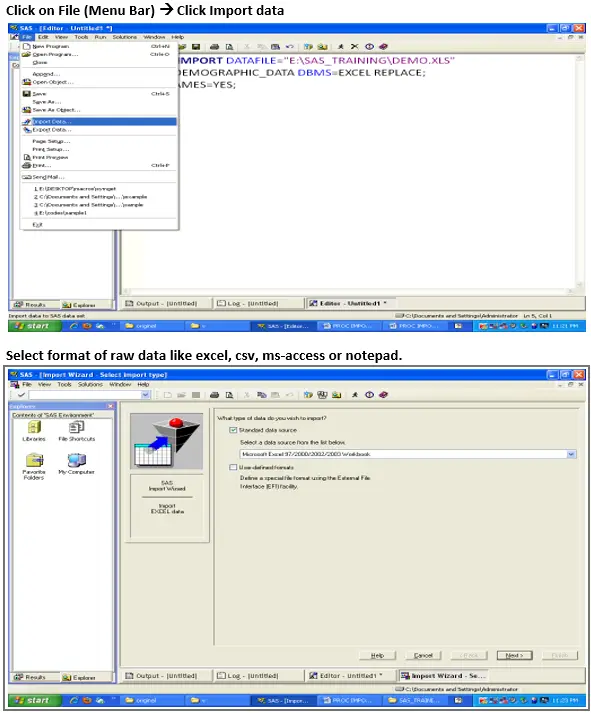
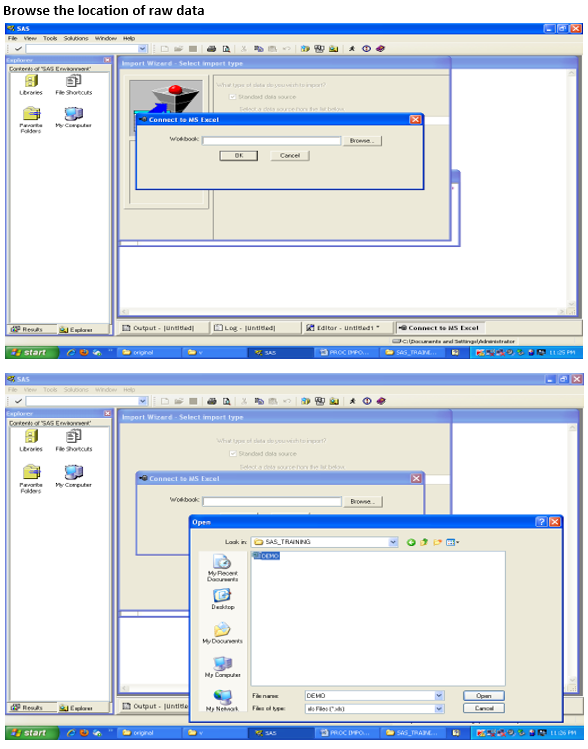
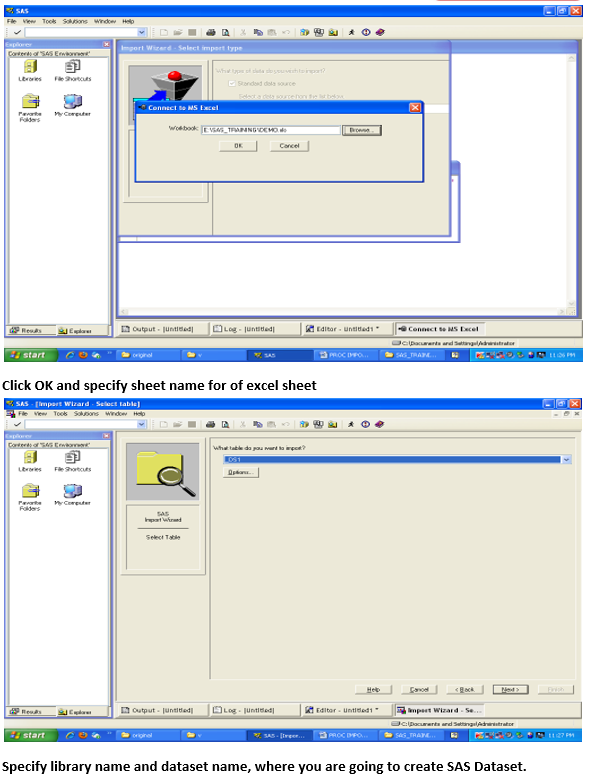
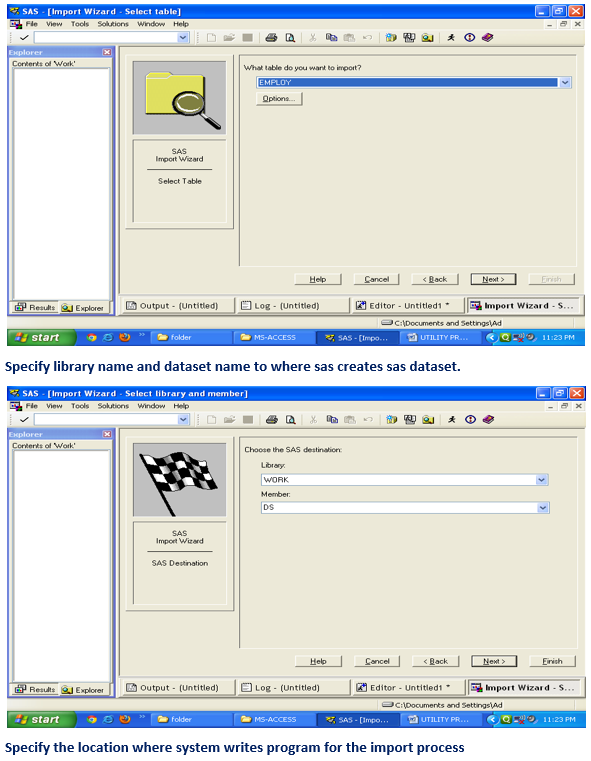
When you run the IMPORT procedure, it reads the input file and writes the data to a SAS data set. The SAS variable definitions are based on the input records.
When the IMPORT procedure reads a delimited file, it generates a DATA step code to import the data.
Data WORK.Dataset;
%let _EFIERR_ = 0; /* set the ERROR detection macro variable */
Infile ‘C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator\Desktop\Demo.csv’ delimiter = ‘,’
MISSOVER DSD lrecl=32767 firstobs=2;
Informat EMP_ID $5. ;
Informat EMP_NAME $10. ;
Informat SEX $1. ;
Informat AGE best32. ;
Informat EDUCATION $2. ;
Informat HEIGHT $7. ;
Informat WEIGHT best32. ;
Informat BLOOD_GROUP $4. ;
Informat DOB DATE9. ;
Informat DOJ DATE9. ;
Informat ZONE $6. ;
Informat ZONAL_HEAD $13. ;
Informat REGION $11. ;
Informat REGIONAL_MANAGER $22. ;
Informat INCOME best32. ;
Format EMP_ID $5. ;
Format EMP_NAME $10. ;
Format SEX $1. ;
Format AGE best12. ;
Format EDUCATION $2. ;
Format HEIGHT $7. ;
Format WEIGHT best12. ;
Format BLOOD_GROUP $4. ;
Format DOB DATE9. ;
Format DOJ DATE9. ;
Format ZONE $6. ;
Format ZONAL_HEAD $13. ;
Format REGION $11. ;
Format REGIONAL_MANAGER $22. ;
Format INCOME best12. ;
Input EMP_ID $
EMP_NAME $
SEX $
AGE
EDUCATION $
HEIGHT $
WEIGHT
BLOOD_GROUP $
DOB
DOJ
ZONE $
ZONAL_HEAD $
REGION $
REGIONAL_MANAGER $
INCOME
;
If _ERROR_ then call symputx(‘_EFIERR_’,1); /*set ERROR detection macro variable*/
Run;
