Proc Contents :
Proc contents gives descriptive information for all variables found in SAS dataset such as type, length, position, format, informat and label.
Using this procedure we can see description information of dataset.
It is useful for document purpose. (Documenting SAS datasets stored in libraries)
Syntax:-
PROC CONTENTS <OPTIONS>;
RUN;
Examples:-
PROC CONTENTS;
RUN;
It prints content information for latest dataset.
Options:-
Data: – Specify the input data set for which dataset we are finding descriptor information.
PROC CONTENTS DATA=SASHELP.CLASS;
RUN;
Out: – Specify the output data set
It creates description information portion in output dataset.
PROC CONTENTS DATA=SASHELP.CLASS OUT=WORK.DATASET;
RUN;
Noprint: – Suppress the printing of the output
PROC CONTENTS DATA= DATA=SASHELP.CLASS OUT=DATASET NOPRINT;
RUN;
Position: – Default variables in the dataset are printed out an alphabetic order, when this position option specified, a second list of variables is output according to their position in the dataset.
PROC CONTENTS DATA=SASHELP.CLASS POSITION;
RUN;
But don’t want in Alphabetic order, Need only list of variables with their attributes in dataset order use
Varnum: – Print a list of the variables by their logical position in the data set
PROC CONTENTS DATA=SASHELP.CLASS VARNUM;
RUN;
Short: – Prints out only names of variables (without attributes) in SAS dataset.
PROC CONTENTS DATA=SASHELP.CLASS SHORT;
RUN;
Default it prints list of variables in Alphabetical order, but need to print in both alphabetic and dataset order
PROC CONTENTS DATA=SASHELP.CLASS SHORT POSITION;
RUN;
Default it prints list of variables in Alphabetic order, but need to print in only dataset order
PROC CONTENTS DATA=SASHELP.CLASS SHORT /*POSITION*/ VARNUM;
RUN;
Centiles: – Print centiles information for indexed variables
/*SIMPLE INDEX */
PROC SQL;
CREATE INDEX NAME ON SASHELP.CLASS (NAME);
QUIT;
/* COMPOSITE INDEX*/
PROC SQL;
CREATE INDEX NAME ON SASHELP.CLASS (NAME,SEX,AGE,HEIGHT,WEIGHT);
QUIT;
PROC CONTENTS DATA= SASHELP.CLASS CENTILES;
RUN;
Out2:- Specify the name of an output data set to contain information about indexes and integrity constraints
PROC CONTENTS DATA= SASHELP.CLASS OUT =DATASET1 OUT2=DATASET2;
RUN;
Data=_all_:- Prints descriptor information for all the datasets in library.
PROC CONTENTS DATA=WORK._ALL_;
RUN;
Nods:-Suppress the printing of individual files
NODS can use with only DATA=_ALL_.
PROC CONTENTS DATA=WORK._ALL_ NODS;
RUN;
Fmtlen: – Print the length of a variable’s informat or format
PROC CONTENTS DATA= SASHELP.CLASS FMTLEN;
RUN;
Directory: – Print a list of the SAS files in the SAS library
PROC CONTENTS DATA= SASHELP.CLASS DIRECTORY;
RUN;
Order: – COLLATE | CASECOLLATE | IGNORECASE | VARNUM
Collate – Prints list of variables in alphabetical order beginning with uppercase and then lowercase names.
Casecollate – Prints list of variables in alphabetic order even if they include mixed-case names and numerics.
Ignorecase – Prints list of variables in alphabetical order ignoring the case of letters.
Varnum – It is same like Varnum option (means prints variables in dataset order).
PROC CONTENTS DATA= SASHELP.CLASS ORDER=VARNUM;
RUN;
Memtype: –
The contents statement produces output only for member types like DATA, VIEW, and ALL, which includes DATA and VIEW.
PROC DATASETS MEMTYPE=DATA;
CONTENTS DATA=SASHELP._ALL_;
RUN;
PROC DATASETS MEMTYPE=DATA;
CONTENTS DATA=SASHELP._ALL_;
RUN;
To get contents off all catalogs
PROC CONTENTS MEMTYPE=LIB.CATALOG;
RUN;
To get contents off all Views
PROC CONTENTS MEMTYPE=LIB.VIEW;
RUN;
How can you Calculate Data Set Size
To estimate the amount of disk space that is needed for a SAS data set:
Create a dummy SAS data set that contains information from sashelp.class (which contains 19 observations and 5 variables) that you need run the CONTENTS procedure using the dummy data set
Determine the data set size by performing simple math using information from the CONTENTS procedure output.
DATA DS;
SET SASHELP.CLASS;
RUN;
PROC CONTENTS DATA=DS;
TITLE ‘EXAMPLE FOR CALCULATING DATA SET SIZE’;
RUN;
These statements generate the output shown in Example for Calculating Data Set Size with PROC CONTENTS.
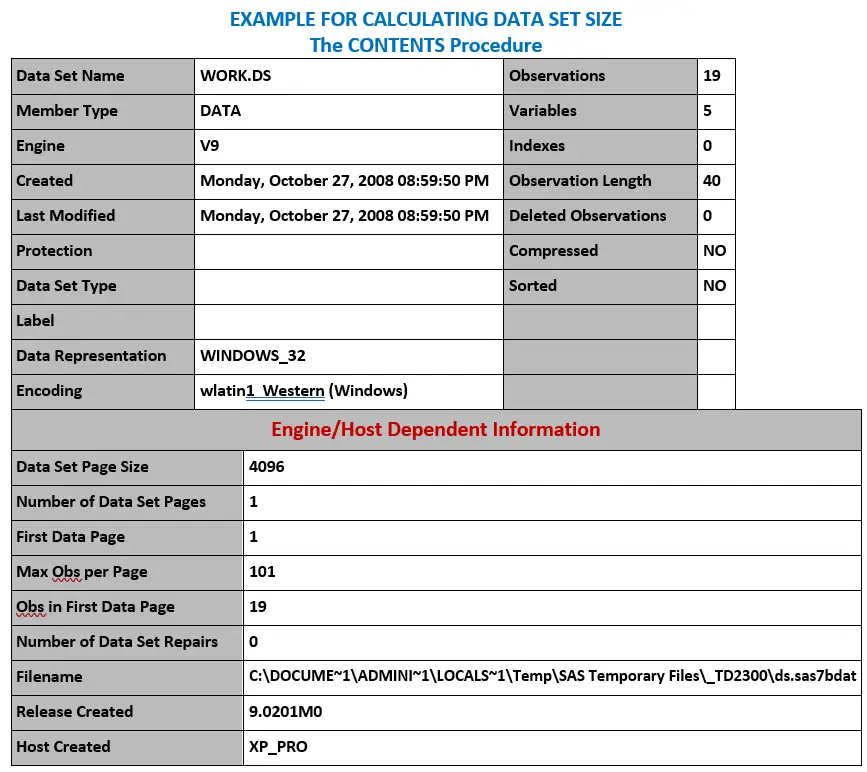
The size of the resulting data set depends on the data set page size and the number of observations. You can use your PROC CONTENTS output and the following formula to estimate the data set size:
Number of data pages = 1 + (floor (Observations / Max Obs per Page))
Size = 256 + (Data Set Page Size * number of data pages)
(Floor represents a function that rounds the value down to the nearest integer.)
Taking the information that is shown in Example for Calculating Data Set Size with PROC CONTENTS, you can calculate the size of the example data set:
Number of data pages = 1 + (floor(1/101))
Size = 256 + (4096 * 1) = 4352
Thus, the example data set uses 4,352 bytes of storage space.
