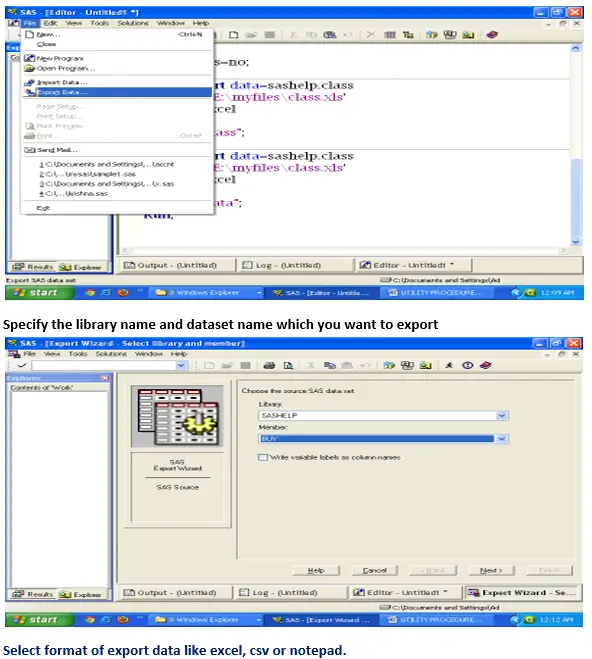
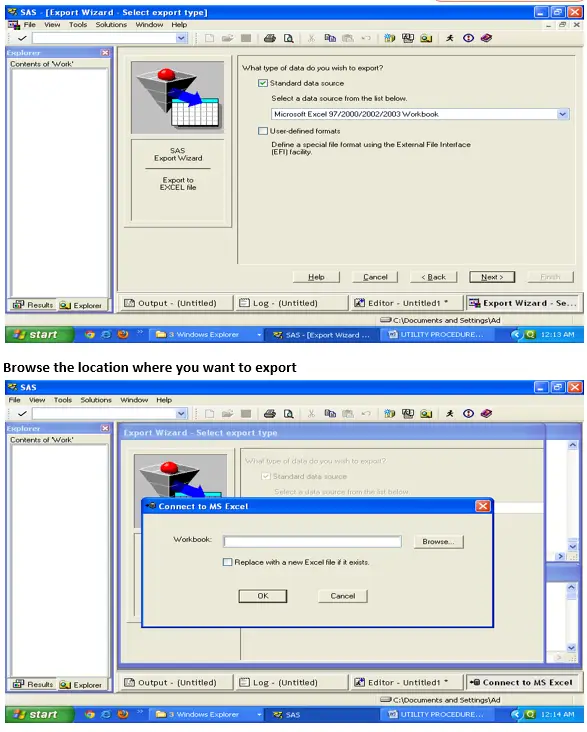
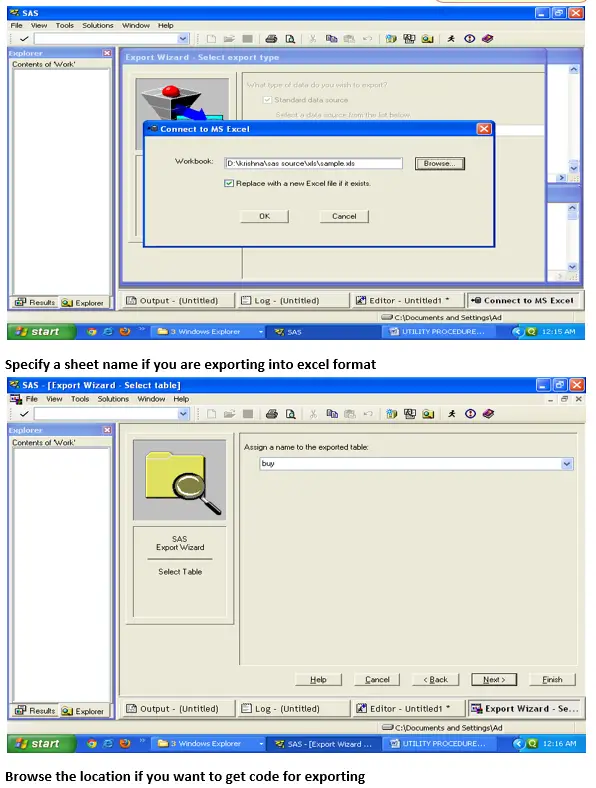
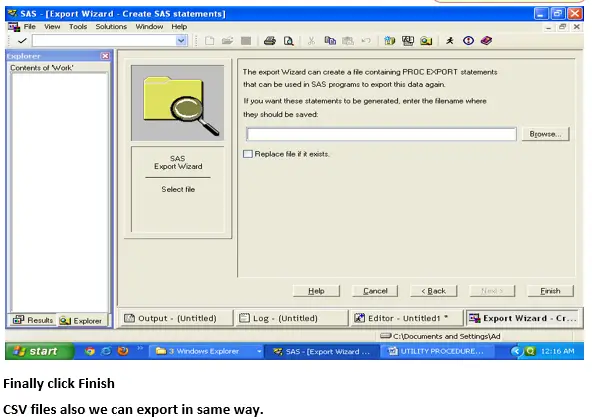
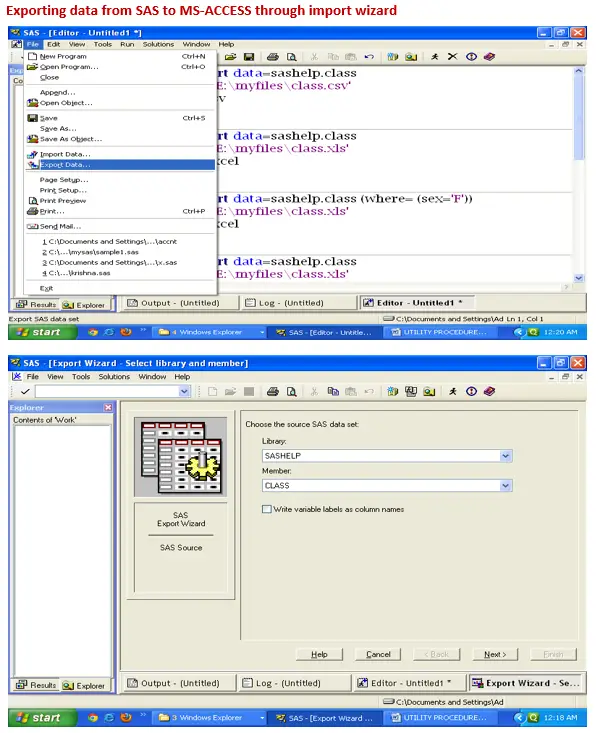
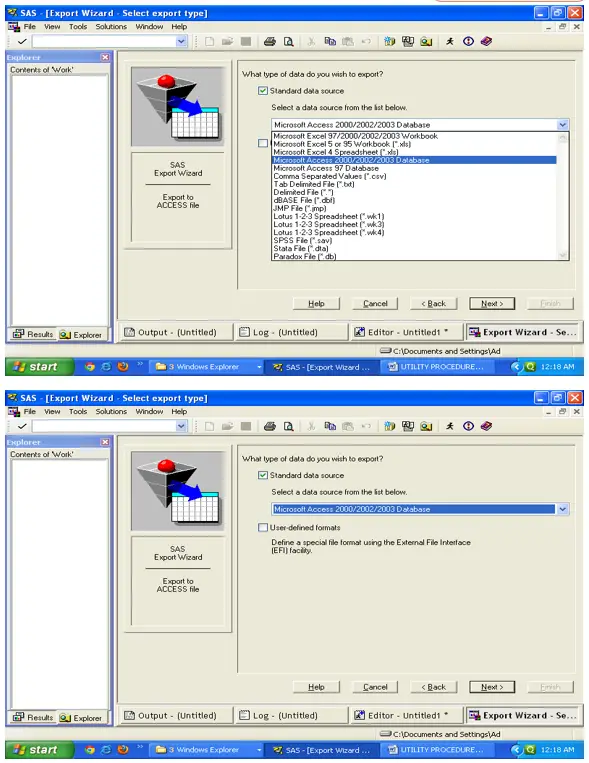
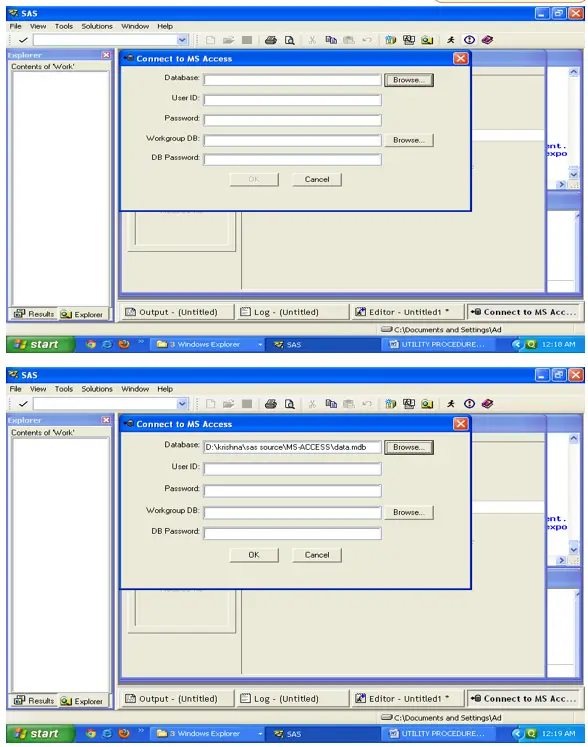
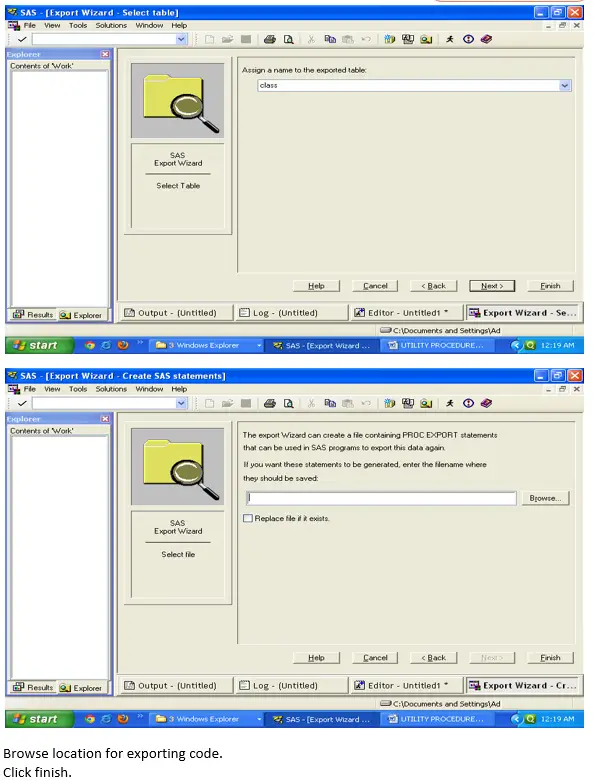
Proc Export :
PROC EXPORT reads data from a SAS data set and writes it to an external data
source. External data sources can include such files as Microsoft Access Databases,
Microsoft Excel Workbooks, Lotus spreadsheets, and delimited files. In delimited files,
A delimiter such as a blank, comma, or tab separates columns of data values.
Syntax:-
PROC EXPORT DATA=<LIBREF.>SAS DATA-SET <(SAS DATA-SET-OPTIONS)>
OUTFILE=”FILENAME” | OUTTABLE=”TABLENAME”
<DBMS=IDENTIFIER> <LABEL><REPLACE>;
PUTNAMES=YES/NO;
SHEET=”SHEET_NAME”;
RUN;
Examples:-
Data=Dataset
Specify the dataset name which we are exporting into external files.
Outfile=File location
Specify the file location to where we are exporting data
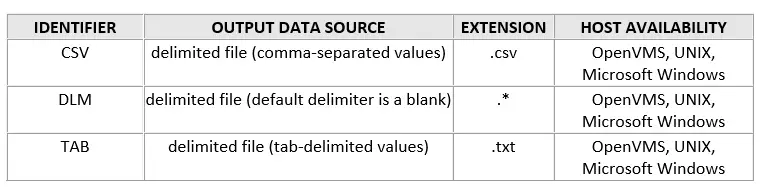
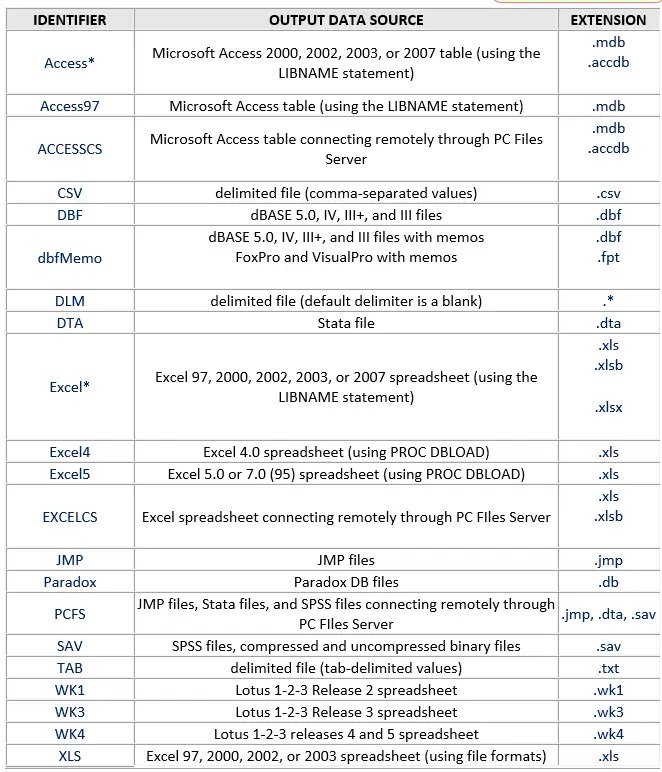
DBMS=File identifier
Specify the DBMS (type of data) of external file.
PROC EXPORT DATA=SASHELP.CARS
OUTFILE=’E:\MYFILES\CLASS.XLS’
DBMS=EXCEL;
RUN;
PROC EXPORT DATA=SASHELP.CLASS
OUTFILE=’C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator\Desktop\sas\CLASS.TXT’
DBMS=TAB;
RUN;
Label
Writes SAS label names as column names to the exported table. If SAS label names do not exist, then the variable names are used as column names in the exported table.
DATA DS;
SET SASHELP.CLASS;
LABEL SEX=GENDER;
RUN;
PROC EXPORT DATA=ds
OUTFILE=’E:\MYFILES\CLASS.XLS\CLASS.XLS’
DBMS=EXCEL
LABEL; /*Check once without label*/
RUN;
Replace
If already external file exists it replaces on that. Default is noreplace.
PROC EXPORT DATA=ds
OUTFILE=’E:\MYFILES\CLASS.XLS\CLASS.XLS’
DBMS=EXCEL
LABEL
REPLACE;
RUN;
Putnames=Yes/No
Default is Yes, It means it writes column names in external file when we export data.
But if we specify Putnames=No, It won’t write columns in external file.
PROC EXPORT DATA=DS
OUTFILE=’C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator\Desktop\sas\CLASS.TXT’
DBMS=TAB
REPLACE;
PUTNAMES=NO;
RUN;
Sheet=”Sheet Name”
Specify the Sheet name in excel file, in which sheet we are writing the data.
In same excel file we are exporting data into multiple sheets
PROC EXPORT DATA=SASHELP.CLASS
OUTFILE=’C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator\Desktop\sas\CLASS.XLS’
DBMS=EXCEL
LABEL
REPLACE;
SHEET=”KRISHNA”;
RUN;
PROC EXPORT DATA=SASHELP.CARS
OUTFILE=’C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator\Desktop\sas\CLASS.XLS’
DBMS=EXCEL
LABEL
REPLACE;
SHEET=”STANSYS”;
RUN;
OUTTABLE=table-name
Specifies the DBMS output table. If the name does not include special characters (such as question marks), lowercase characters, or spaces, omit the quotation marks. The DBMS table name might be case sensitive.
PROC EXPORT OUTTABLE=CLASS
DATA=SASHELP.CLASS
DBMS=ACCESS
REPLACE;
DATABASE=”C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator\Desktop\New Folder\STANSYS\HYDERABAD\SAS\SOURCE DATA\MS-ACCESS\DATA.MDB”;
RUN;
Exporting data into CSV file
PROC EXPORT DATA=SASHELP.CLASS
OUTFILE=’E:\MYFILES\CLASS.CSV’
DBMS=CSV
REPLACE;
RUN;
Exporting data into EXCEL file
PROC EXPORT DATA=SASHELP.CLASS
OUTFILE=’E:\MYFILES\CLASS.XLS’
DBMS=EXCEL
REPLACE;
PUTNAMES=YES;
SHEET=”SAMPLE”;
RUN;
PROC EXPORT DATA=SASHELP.CLASS (WHERE= (SEX=’F’))
OUTFILE=’E:\MYFILES\CLASS.XLS’
DBMS=EXCEL
REPLACE;
RUN;